Ask | Share | Grow™ - Question & Answer Community
Of the Members, By the Members, For the Members!
VacuumFurnaces.com is a Q&A community where vacuum furnace product and service suppliers connect with commercial and captive heat treaters to share their practical skills and know-how and to establish valuable relationships around niche topics of expertise with vacuum furnace end-users in operations, production, training, maintenance, marketing, sales, and engineering.

Can a thermocouple be twisted?
Per AMS2750F, thermocouples can be twisted or bead welded as long as no filler material is used. Proper procedures in constructing either hot junctions is imperative.
Per AMS2750F, thermocouples can be twisted or bead welded as long as no filler material is used. Proper procedures in constructing either hot junctions is imperative.
See lessWhat is a vacuum furnace bakeout?
Bake-out is a process which is meant to remove contaminants from components so that high vacuum can be achieved in treatment, and to prevent impurities. To remove these unwanted compounds, engineers perform bake-outs at various high temperatures (these can range from 120 degrees Celsius up to 400 deRead more
Bake-out is a process which is meant to remove contaminants from components so that high vacuum can be achieved in treatment, and to prevent impurities. To remove these unwanted compounds, engineers perform bake-outs at various high temperatures (these can range from 120 degrees Celsius up to 400 degrees Celsius).
The volatile compounds (such as vapor from components, or external particulate matter from humans or the environment) are driven off of the component during the period of heating. The volatile particles are then removed by the vacuum pump.
References:
Vacuum Bake Out: Its Importance and Implementation
courtesy of Vacuum Science World
https://www.vacuumscienceworld.com/blog/vacuum-bake-out
See lessWhat are the 3 stages of quenching?
The 3 stages of quenching are the Vapor Stage, the Boiling Stage, and finally the Convection stage. These stages are in reference to the interaction between the quenchant and the component being cooled. Vapor Stage: In this stage the super-heated component immediately vaporizes the quenchant. The gaRead more
The 3 stages of quenching are the Vapor Stage, the Boiling Stage, and finally the Convection stage. These stages are in reference to the interaction between the quenchant and the component being cooled. Vapor Stage: In this stage the super-heated component immediately vaporizes the quenchant. The gaseous quenchant now surrounds the component in a thin sheet, and the liquid quenchant is no longer in contact with the component and the heat therefore slowly seeps out of the component by radiation and limited conduction. Boiling Stage: As the vapor insulation degrades and collapses, the component begins to boil the quenchant. Due to the direct contact with the liquid quenchant, cooling occurs quicker than the vapor stage. Eventually, as the heat diffuses into the liquid, the interface temperature drops below boiling and the convection stage begins. This is a similar principle to that which allows this to occur (see video). This is called the Leidenfrost Effect (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leidenfrost_effect#:~:text=The%20Leidenfrost%20effect%20is%20a,the%20liquid%20from%20boiling%20rapidly.) Convection Stage: Finally, the convection stage occurs after boiling has ceased and the heat can only be transferred by convection. The rate of cooling gradually decays as the system approaches equilibrium. Please see the graphical illustration below.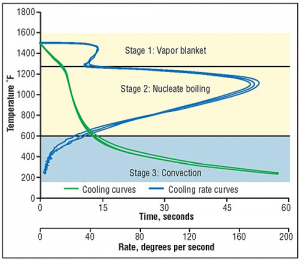 Image courtesy of Globalspec.com
Image courtesy of Globalspec.com
References: Understanding the Cooling Curve Test by D. Scott MacKenzie courtesy of Thermal Processing Magazine https://www.houghtonintl.com/sites/default/files/resources/article_-_understanding_the_cooling_curve_test_0.pdf
See less
Why is carburizing less expensive than nitriding?
While both procedures have the same end goal of surface hardening components, nitriding and carburizing employ different resources and methods to do so, with different results. Carburizing is a heat treat process that uses carbon, while Nitriding uses nitrogen. Generally, each process diffuses the cRead more
While both procedures have the same end goal of surface hardening components, nitriding and carburizing employ different resources and methods to do so, with different results. Carburizing is a heat treat process that uses carbon, while Nitriding uses nitrogen. Generally, each process diffuses the chosen element into the surface of the component to produce a more wear resistant or harder surface. Nitriding is a better process for precision components, whereas carburizing may be a better choice for highly loaded coarse components [1].
Nitriding sometimes results in higher costs primarily because of cycle times and batch processing considerations. However, the cost increase typically corresponds to better properties. Another driver of cost is the cost of the base material. Nitrided steels tend to be produced from high alloy steels, which are usually more expensive [2].
In some cases, the carburizing process may prove more expensive, but the price of the base material (likely high alloy) must also be factored in [1][2].
[1]-https://blog.metlabheattreat.com/posts/nitriding-and-carburizing/#:~:text=The%20main%20difference%20is%20that,in%20carburizing%2C%20carbon%20is%20used.&text=Ion%20nitriding%2C%20on%20the%20other,is%20a%20more%20restrictive%20process.
[2]-https://www.eurotherm.com/en/heat-treatment-articles-en/what-is-the-cost-difference-between-carburizing-and-nitriding/#:~:text=For%20Carburized%20steels%20you%20would,processing%20and%20long%20cycle%20times.
See lessHow does a vacuum furnace roughing pump work?
The roughing pump is the component that primes the other pumps in series on the vacuum line, evacuating the system until a pressure level is reached at which a booster pump (known as a lobe-type roots pump) can be activated, followed by other types of diffusion, turbo molecular, cryogenic, ionic andRead more
The roughing pump is the component that primes the other pumps in series on the vacuum line, evacuating the system until a pressure level is reached at which a booster pump (known as a lobe-type roots pump) can be activated, followed by other types of diffusion, turbo molecular, cryogenic, ionic and other pumps that can be used when the pressure is reached.
Depending on the flow rate, the pumping system is proportioned in relation to system volume, pumping cycle speed, load degassing and contamination produced by the load (vapors, dust, binders, etc.) in the pump itself. It is for this reason that mechanical strength and wear influence the choice of pump type.
I highly recommend you to read an intersting article (splitted in two parts) about this topic:
Roughing pump in high-vacuum furnaces for beginners [1/2]
Roughing pump in high-vacuum furnaces for beginners [2/2]
See lessWhat is a 2-bar vacuum furnace vs. 6-bar vacuum furnace?
The term 2-bar is typically describing the quenching pressure capability of the furnace. A 2-bar operates (quenches) at 2-bar or 15 psig. A 6-bar would of course be operating at 6-bar when quenching. Typically quenching pressures are selectable and the ratings would be the maximum operating pressuRead more
The term 2-bar is typically describing the quenching pressure capability of the furnace. A 2-bar operates (quenches) at 2-bar or 15 psig. A 6-bar would of course be operating at 6-bar when quenching. Typically quenching pressures are selectable and the ratings would be the maximum operating pressures.
See lessCan a vacuum heat treat furnace be considered in a confined space?
Yes a vacuum furnace or any similar chamber can be considered a confined space. A confined space is any space with limited entry or egress. The primary concern in a vacuum furnace (confined space) is limited air flow or available oxygen to breathe. With vacuum furnaces we also have to consider theRead more
Yes a vacuum furnace or any similar chamber can be considered a confined space. A confined space is any space with limited entry or egress. The primary concern in a vacuum furnace (confined space) is limited air flow or available oxygen to breathe. With vacuum furnaces we also have to consider the fact that process gasses are also connected to the furnace or vessel. These gasses can also displace oxygen when used during back-fill or if leaking.
See lessHow to clean vacuum brazing furnace chamber after oxidation?
Here is and article about the cleanup of a contaminated Vacuum Furnace: https://vacaero.com/information-resources/vac-aero-training/7001-cleanup-contaminated-vacuum-furnaces.html
Here is and article about the cleanup of a contaminated Vacuum Furnace:
https://vacaero.com/information-resources/vac-aero-training/7001-cleanup-contaminated-vacuum-furnaces.html
See lessWhy do thermocouples start to deviate in temperature over time?
Time and temperature have a way of making things deteriorate. Vacuum also can present a problem for the materials (constituents) of the thermocouple, specifically relating to the vapor pressure of the materials.
Time and temperature have a way of making things deteriorate. Vacuum also can present a problem for the materials (constituents) of the thermocouple, specifically relating to the vapor pressure of the materials.
See lessHow to control the current for molybdenum heating elements?
First work a little bit "feed forward" and monitor the resistance carefully, since it changes with the temperature of the element. When the resistance is somewhat stabilized: release more power. We have thyristor control units for driving Molibdenum elements. They can also drive Tungestenum, KanthalRead more
First work a little bit “feed forward” and monitor the resistance carefully, since it changes with the temperature of the element.
When the resistance is somewhat stabilized: release more power.
We have thyristor control units for driving Molibdenum elements. They can also drive Tungestenum, KanthalSuper, Platinum and Silicium-Carbide (SiC), as well as quartz lamps and short-wave infraled loads.
See: thyristor modules for molubdenum
See lessAre there any examples of touch screen furnace controllers?
Yes there is. Check our heatmanager pro system. A flexible control system for 6 (or 12) channels. The system combines both the control & registration in 1 system. So no separate recorder needed. Used by many heat-treaters around the world. See attached the brochure.HeatManagerPro_5.01
Yes there is.
Check our heatmanager pro system. A flexible control system for 6 (or 12) channels. The system combines both the control & registration in 1 system. So no separate recorder needed.
Used by many heat-treaters around the world.
See attached the brochure.HeatManagerPro_5.01
See lessHow are thermocouples attached to a part during heat treatment?
Thermocoupe wires stripped and at the end twisted into each other: this where the metals touch is the measurement point. Then the wire is put somewhere around or on the product. Tip: use thermcouple wire with calibration certificate. See: https://cascade.net/en/thermocouple/
Thermocoupe wires stripped and at the end twisted into each other: this where the metals touch is the measurement point. Then the wire is put somewhere around or on the product.
Tip: use thermcouple wire with calibration certificate.
See: https://cascade.net/en/thermocouple/
See lessHow can you speed up the response time of a temperature probe?
a) Use thinner thermocouples. b) use a controller that measures faster. Like our RKC Instrument GZ900 controller, that performs 100 measurements & PID calculations per second. RKC Instrument GZ900
a) Use thinner thermocouples.
b) use a controller that measures faster. Like our RKC Instrument GZ900 controller, that performs 100 measurements & PID calculations per second.
RKC Instrument GZ900
See lessHow do you perform a helium leak test on a vacuum furnace?
Finding leaks in vacuum furnaces is a task that few people look forward to, however it is important and necessary. Leaks happen almost always and can occur suddenly or develop over time. They can damage both the material being heat treated as well as internal furnace components. When left uncheckedRead more
Finding leaks in vacuum furnaces is a task that few people look forward to, however it is important and necessary. Leaks happen almost always and can occur suddenly or develop over time. They can damage both the material being heat treated as well as internal furnace components. When left unchecked leaks will stop the furnace from pumping down and will compromise the heating elements. Small leaks often go undetected since the pumping system can overcome them, but they can still cause continuous and eventually catastrophic damage. It is therefore highly recommended that routine leak checking and repair be a part of any good preventative furnace maintenance program.
An Excerpt: “Why is helium used to detect leaks? Helium is used as a tracer gas to detect leaks for several reasons. These include the fact that it constitutes only ~ 5 ppm in air so that background levels are very low. Helium has also relatively low mass so that it is ‘mobile’ and is completely inert/non-reactive. Helium is also non-flammable and generally widely available and low cost. This association with helium is one of the reasons why one of the most accurate and rapid leak detection methods employs helium as the tracer gas and a mass spectrometer for the analyzing/measuring. Furthermore, helium is chosen as a tracer gas because it is light, very quick, and absolutely harmless.” >> Continue Reading
See lessWhat is a gas ballast valve on a vacuum pump?
The gas ballast valve on a mechanical oil-sealed rotary vacuum pump is a very simple device that offers several potential benefits for vacuum pump users and when used correctly can keep a vacuum pump working well. However, gas ballast valves but are often overlooked and are poorly understood, this aRead more
The gas ballast valve on a mechanical oil-sealed rotary vacuum pump is a very simple device that offers several potential benefits for vacuum pump users and when used correctly can keep a vacuum pump working well. However, gas ballast valves but are often overlooked and are poorly understood, this article helps take some of the guesswork out.
An excerpt: “When pumping atmospheric air (or gas) in a vacuum system, however “pure” it may appear to be, it will invariably contain some vapor. During the compression process in the pump, this vapour will condense. Failure to remove it will form a contaminant which will prevent the pump from achieving its optimum vacuum pressure. Also, the condensate can enter the pump’s mechanism, for example the oil in oil-sealed rotary pumps, where, as a contaminant, it can have a detrimental effect.” >> Continue Reading
See less